Lesson 1.1 – Handwashing Hygiene
Hand Disinfection
Look at the following pictures of poorly washed hands (back of the hand, and the palm).
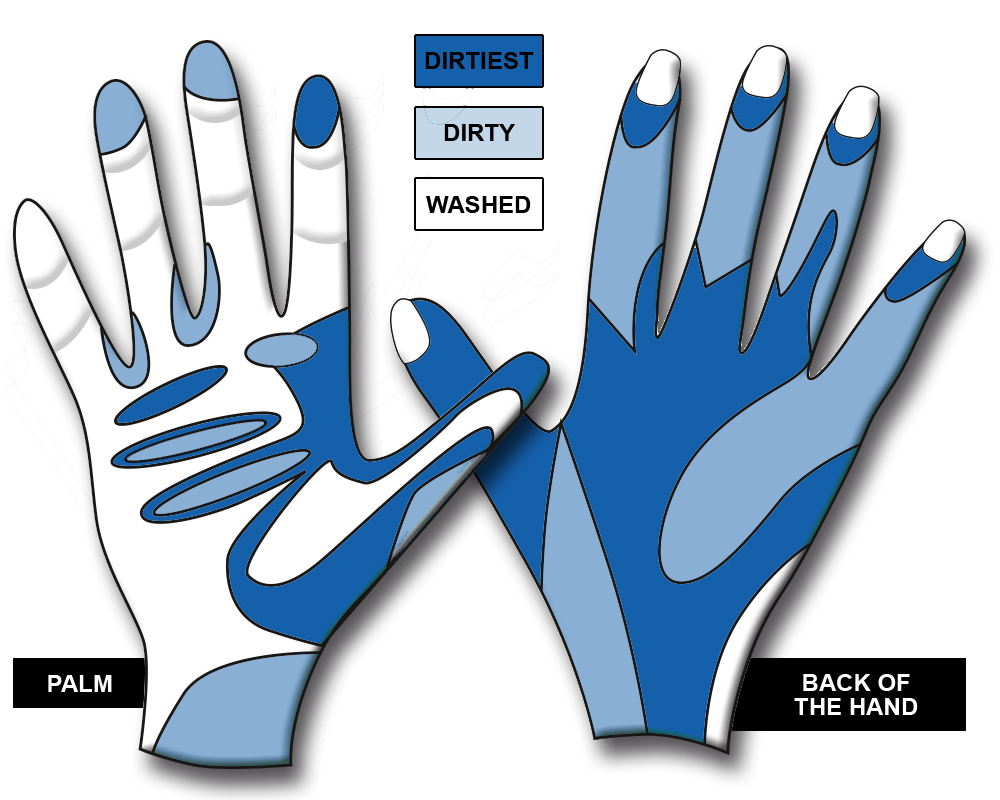
Reflection Exercise:
1. Which parts of the hand are dirty or the dirtiest?
2. Then look at the pictures of handwashing and disinfection.
3. Reflect by using your own hands, how to wash the dirty parts (in the middle of the palm, between the fingers, and fingertips).
4. What could be the right amount of time for rubbing hands? (The right answer can be found in the hand disinfection picture: ... seconds.)
Handwashing

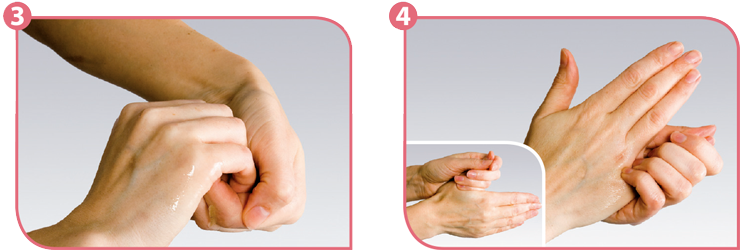
- Rinse hands with tepid water (picture above).
- Apply a dose of washing liquid.
NB: Even more practical way of closing the tap is to use your elbow. - Wash hands thoroughly. Wash also the fingertips.
- Rinse hands (picture below).
- Dry off your hands by dabbing thoroughly, do not rub.
- Close the tab with a paper towel.

Hand Disinfection

Hand Care
There are two main points to taking care of your hands:
Remove your watch and rings when you are working. Dirt, chemicals, and detergents accumulate under them. That is why they must be removed while working.
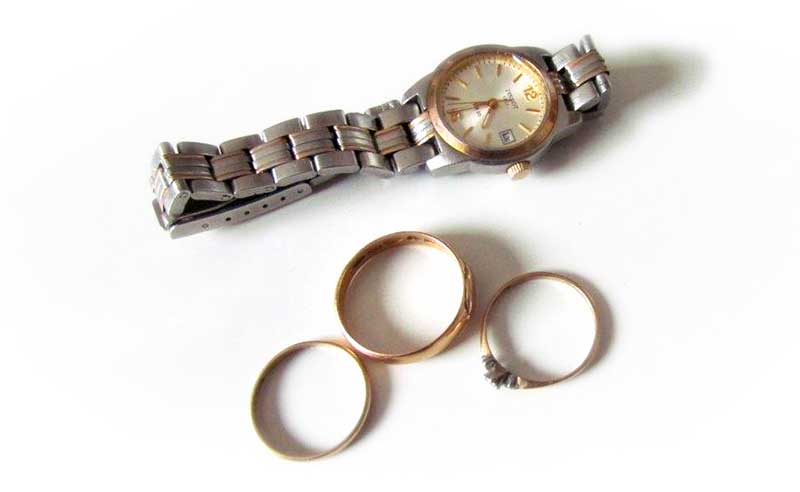

Dirt, chemicals, and detergents accumulate under the watch and rings.
Wash your hands with warm water. Use a mild detergent.
Strong detergents irritate the skin. Long-term use may cause allergies.
Do not pick or cut your nail walls.
Nail wall is the part of the skin where the nail meets the skin of the finger (1).
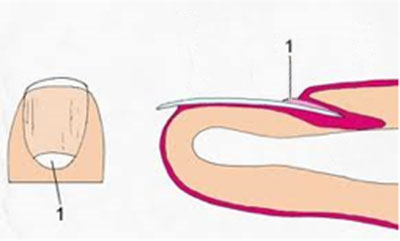
If the nail walls are broken, bacteria will get under them and they become infected.
Use only disposable hand towels. If there is a dispenser that uses cloth roll towels, replace the old roll with a new one as soon as the old one is used.
For example in hospitals, the employees' hand hygiene is closely monitored. A sample may be taken after handwashing. The sample is called a Petri dish sample. It can be taken e.g. after a month of employment.
The sample is put into culture. Culture is used for studying microbes and their growth. When the results are ready they will be reviewed with the employee.
If the sample contains more than the usual amount of microbes, the employee's handwashing habits and the proper way of handwashing will be discussed with the employee. Municipal health protection authorities can provide Petri dishes and help reading the results.

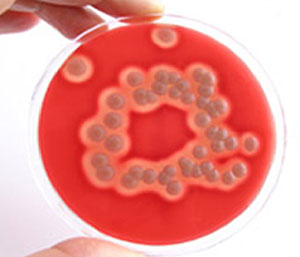
The sample is taken from the surface of a table. On the right: a dirty sample. One colony has formed around a single microbe while it was dividing.
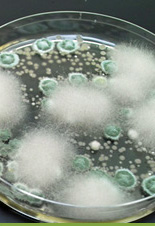
Cross-contamination may sometimes occur in hospitals if they are using shared soaps and towels. Cross-contamination is further discussed in lesson 5.

Very good hygiene is needed when handling cooked meat, fish, and eggs, and the food will not be heated again. It is also needed if you cut your hand. Picture: Ruokatieto (Food Knowledge)/Jussi Ulkuniemi
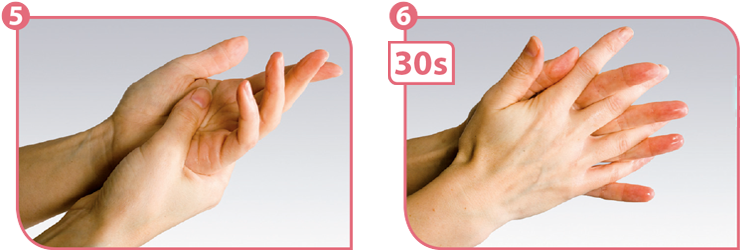
Shared soaps, towels, and nail brushes should not be used because of cross-contamination. In some tasks hand washing is not enough and you have to wear disposable gloves. The gloves must be changed every half an hour because of hand perspiration. Soap removes visible dirt from the hands. Invisible dirt can be removed with alcohol-based hand rub that contains glycerol.

Hand rub is rubbed into clean and dry hands. The hands have to be rubbed for about 30 seconds.
Always wash your hands:- with soap and warm water before starting to work
- after handling bad i.e. contaminated foodstuffs
- after handling e.g. raw meat, poultry, or root vegetables that contain soil
It is important that you wash your hands regularly while you are handling raw foodstuffs or dirty utensils, for example bloody knives.
Wash your hands after every time you do something that is not part of your work. In other words, wash your hands after every time you eat, drink, smoke a cigarette, shake someone's hand, wipe your nose, handle money, or use the toilet.
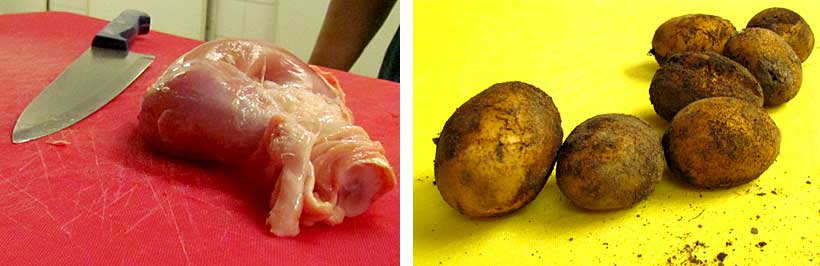
Wash your hands after handling raw meat, especially poultry, and foodstuffs that contain soil. Root vegetables should be washed in a separate washing bowl.
Source (from where the Handwashing text is shortened and adapted): Välikylä, Tapio and Syyrakki, Sara (2013) Hygieniaopas (Hygiene Guide). Publisher: Elintarvike ja Terveys (Foodstuff and Health) magazine.
Sivusto on selkokielinen sitä on helppo ymmärtää.



